gin-gonic/gin 源码分析
Gin
知名 web 框架一览
https://github.com/mingrammer/go-web-framework-stars
案例
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
g := gin.Default()
// 用户主动用的 MVC 模式
ctl := &UserController{}
g.GET("/user", ctl.GetUser)
g.Run(":8080")
}
type UserController struct {
}
func (c *UserController) GetUser(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.String(200, "hello, world")
}
IRoutes 接口
核心接口 IRoutes:提供的是注册路由的抽象。
Gin 和 Beego 的区别是没有 Controller 的抽象,也就没有了默认的 MVC 模式,这种设计更为灵活。 中间件设计者不需要考虑这种问题,这样框架的使用者就可以按需选用合适的组织架构。
// IRoutes defines all router handle interface.
type IRoutes interface {
// 提供了用户接入自定义逻辑的能力,这个一般情况下也被看做是插件机制。
Use(...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
// 9 种 http 方法
Handle(string, string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
Any(string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
GET(string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
POST(string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
DELETE(string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
PATCH(string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
PUT(string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
OPTIONS(string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
HEAD(string, ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes
// 静态文件的接口
StaticFile(string, string) IRoutes
StaticFileFS(string, string, http.FileSystem) IRoutes
Static(string, string) IRoutes
StaticFS(string, http.FileSystem) IRoutes
}
Engine 实现
type Engine struct {
// 路由组
RouterGroup
// ...
// context 对象池
pool sync.Pool
// 方法路由树
trees methodTrees
// ...
}
- 实现了路由树功能(注册和匹配路由)
- 它本身可以作为一个 Handler 传递到 http 包,用于启动服务器 (Run 方法就是实现这个功能)
// Run attaches the router to a http.Server and starts listening and serving HTTP requests.
// It is a shortcut for http.ListenAndServe(addr, router)
// Note: this method will block the calling goroutine indefinitely unless an error happens.
func (engine *Engine) Run(addr ...string) (err error) {
defer func() { debugPrintError(err) }()
...
address := resolveAddress(addr)
debugPrint("Listening and serving HTTP on %s\n", address)
err = http.ListenAndServe(address, engine.Handler())
return
}
Engine 的路由树功能本质上是依赖于 methodTree 的。
methodTrees 和 methodTree
methodTree 才是真实的路由树。
Gin 定义了 methodTrees,它实际上代表的是森林,即每一个 HTTP 方法都对应到一棵树。
type Engine struct {
...
noRoute HandlersChain
noMethod HandlersChain
pool sync.Pool
// Engine 字段
trees methodTrees
maxParams uint16
maxSections uint16
trustedProxies []string
...
}
type methodTree struct {
method string
root *node
}
type methodTrees []methodTree
HandlerFunc 和 HandlersChain
HandlerFunc 定义了核心抽象 —— 处理逻辑。
在默认情况下,它代表了注册路由的业务代码。
HandlersChain 则是构造了责任链模式。
// HandlerFunc defines the handler used by gin middleware as return value.
type HandlerFunc func(*Context)
// HandlersChain defines a HandlerFunc slice.
type HandlersChain []HandlerFunc
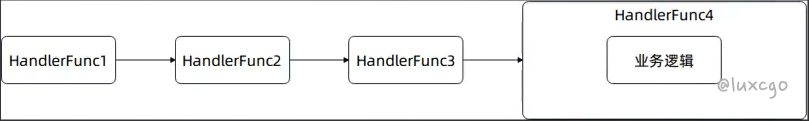
最后一个才是封装了业务逻辑的 HandlerFunc
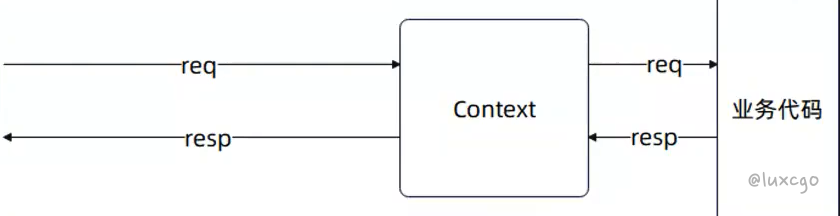
Context 抽象
Context 也是代表了执行的上下文,提供了丰富的 APl:
- 处理请求的 API,代表的是以 Get 和 Bind 为前缀的方法
- 从不同的部位读取数据
AddParam(key, value string)GetStringMapStringSlice(key string) (smss map[string][]string)Param(key string) stringQuery(key string) (value string)DefaultQuery(key, defaultValue string) stringGetQuery(key string) (string, bool)
- Bind 和 ShouldBind 类方法都是将输入转化为一个具体的结构体
Bind(obj any) errorShouldBind(obj any) errorMustBindWith(obj any, b binding.Binding) error
- 从 Keys 里面读取数据
Get(key string) (value any, exists bool)MustGet(key string) any
- 从不同的部位读取数据
- 处理响应的 API,例如返回 JSON 或者 XML 响应的方法
- Gin 的 Context 控制着 Handler 的调度,所以还包含中断后续 Handler 执行的方法
Abort()AbortWithError(code int, err error) *ErrorAbortWithStatus(code int)AbortWithStatusJSON(code int, jsonObj any)
- 返回具体格式的响应
AsciiJSON(code int, obj any)SecureJSON(code int, obj any)JSON(code int, obj any)JSONP(code int, obj any)PureJSON(code int, obj any)XML(code int, obj any)YAML(code int, obj any)TOML(code int, obj any)ProtoBuf(code int, obj any)
- Gin 的 Context 控制着 Handler 的调度,所以还包含中断后续 Handler 执行的方法
- 渲染页面,如 HTML 方法
// Context is the most important part of gin. It allows us to pass variables between middleware,
// manage the flow, validate the JSON of a request and render a JSON response for example.
type Context struct {
writermem responseWriter
Request *http.Request
Writer ResponseWriter
Params Params
handlers HandlersChain
index int8
fullPath string
engine *Engine
params *Params
skippedNodes *[]skippedNode
// This mutex protects Keys map.
mu sync.RWMutex
// Keys is a key/value pair exclusively for the context of each request.
Keys map[string]any
// Errors is a list of errors attached to all the handlers/middlewares who used this context.
Errors errorMsgs
// Accepted defines a list of manually accepted formats for content negotiation.
Accepted []string
// queryCache caches the query result from c.Request.URL.Query().
queryCache url.Values
// formCache caches c.Request.PostForm, which contains the parsed form data from POST, PATCH,
// or PUT body parameters.
formCache url.Values
// SameSite allows a server to define a cookie attribute making it impossible for
// the browser to send this cookie along with cross-site requests.
sameSite http.SameSite
}
路由树实现
Gin 的关键结构体更加直观:
- methodTrees:也就是路由树也是按照 HTTP 方法组织的,例如 GET 会有一棵路由树
- methodTree:定义了单棵树。树在 Gin 里面采用的是 children 的定义方式,即树由节点构成
- node:代表树上的一个节点,里面维持住了 children,即子节点。同时有 nodeType 和 wildChild 来标记一些特殊节点
type Engine struct {
...
trees methodTrees
...
}
type methodTrees []methodTree
type methodTree struct {
method string
root *node
}
type node struct {
path string
indices string
// 通配符
wildChild bool
nType nodeType
priority uint32
children []*node // child nodes, at most 1 :param style node at the end of the array
handlers HandlersChain
fullPath string
}
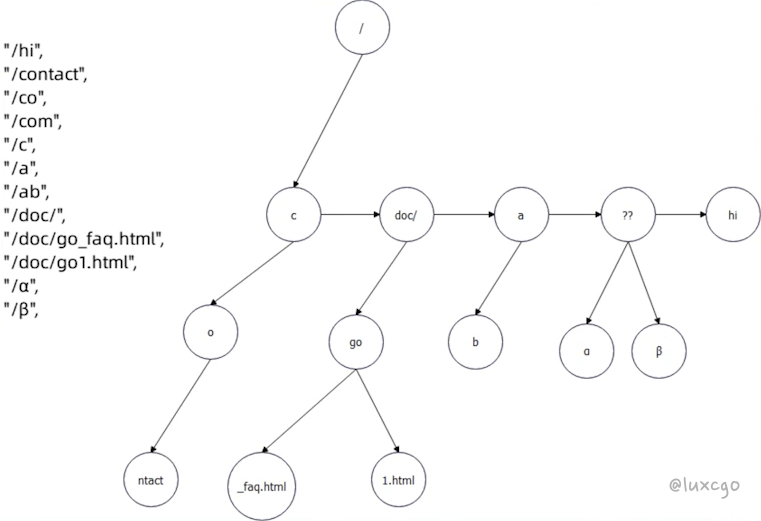
Gin 是利用路由的公共前缀来构造路由树。
AOP 方案
Gin 用的是半集中式设计,由 Context 来调度。但也是实现者在 HandlerFunc 里面主动调用下一个。
type Context struct {
...
handlers HandlersChain
...
}
// HandlersChain defines a HandlerFunc slice.
type HandlersChain []HandlerFunc
// HandlerFunc defines the handler used by gin middleware as return value.
type HandlerFunc func(*Context)
/************************************/
/*********** FLOW CONTROL ***********/
/************************************/
// Next should be used only inside middleware.
// It executes the pending handlers in the chain inside the calling handler.
// See example in GitHub.
func (c *Context) Next() {
c.index++
for c.index < int8(len(c.handlers)) {
if c.handlers[c.index] == nil {
continue
}
c.handlers[c.index](c)
c.index++
}
}
Session 设计
https://github.com/gin-contrib/sessions
是通过嵌入一个 Middleware 来嵌入到请求处理的过程中。
Gin 中 Session 也可以看做是对 gorilla Session 的封装。
gorilla 采用了一种刷新的设计策略。即数据最开始存放在内存,也就是 Values 里面,后面再调用 Save 来真的刷新到存储里面,比如说刷新到 Redis 里面。
抽象总结
- methodTree & node
- HandlerFunc
- Context
- Engine
延伸阅读
- https://go.dev/doc/tutorial/web-service-gin
- 解析 Gin 框架底层原理
- gin框架底层技术原理剖析
- https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin
- https://github.com/gin-gonic/examples

本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。